Jump to a Specific Section
401(k) vs SIMPLE IRA vs SEP IRA: Understanding the Differences and Choosing the Right Retirement Plan
Saving for retirement is a crucial financial decision for both individuals and businesses. Employers often provide retirement plans to attract and retain talent, while individuals seek plans to secure their future. Among the various options available, 401(k) plans, SIMPLE IRAs, and SEP IRAs are popular choices, especially for small business owners and self-employed individuals. Each has unique features, advantages, and considerations.
In this article, we’ll explore the historical context of these plans, their features, tax implications, and how to determine which is right for you or your business.
A Brief History of Retirement Plans
Retirement plans have evolved to meet the needs of both employees and employers:
401(k) Plans
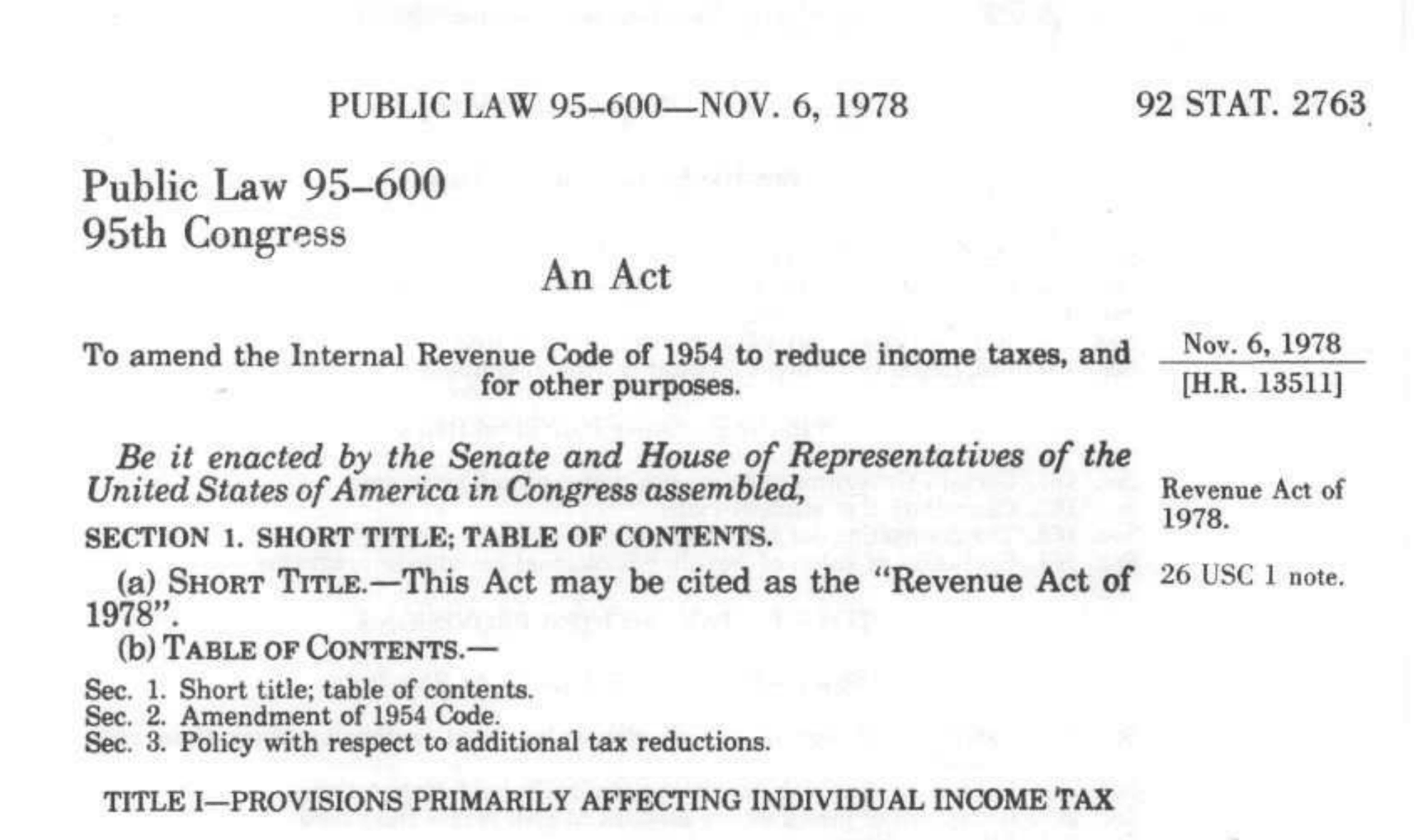
Introduced in 1978 as part of the Revenue Act, 401(k) plans gained popularity in the 1980s as a tax-advantaged alternative to traditional pensions. They allowed employees to defer a portion of their salary into a retirement account.
SIMPLE IRAs
Created in 1996 through the Small Business Job Protection Act, SIMPLE IRAs were designed to provide a simpler, cost-effective retirement savings plan for small businesses.
SEP IRAs
Established in 1978, SEP IRAs (Simplified Employee Pension) were aimed at self-employed individuals and small businesses, offering flexibility in contributions without the administrative burden of traditional pensions.
Understanding these historical contexts helps highlight why these plans were developed and how they cater to different needs.
Key Features of Each Retirement Plan
401(k) Plan
A 401(k) is a defined contribution plan where employees can contribute pre-tax income, and employers may offer matching contributions.
401K Plan Eligibility
Employers of any size can establish a 401(k) plan.
401K Contribution Limits (2025)
- Employee: Up to $23,500 per year for individuals under 50.
- For those aged 50 and above, an additional $7,500 catch-up contribution is allowed.
- A new “super” catch-up contribution of $11,250 (in lieu of the $7,500) is available for employees aged 60 to 63.
- Employer: Combined employer and employee contributions are capped at the lesser of 100% of the employee’s salary or $70,000.
Roth 401(k)
- Employees can make after-tax Roth contributions, which grow tax-free.
- Starting in 2024, Roth 401(k)s are no longer subject to Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs).
401K Plan Vesting
Employer contributions may follow a vesting schedule (e.g., 3-year cliff or 5-year graded).
Administrative Requirements for 401K Plans
- Annual Form 5500 filing with the IRS.
- Non-discrimination testing to ensure fairness between highly compensated employees and others.
Withdrawals from 401Ks
- Penalty-free withdrawals allowed at age 59½.
- Early withdrawals are subject to a 10% penalty plus income tax, with exceptions for hardships.
SIMPLE IRA
The Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE IRA) is tailored for small businesses with 100 or fewer employees.
Simple IRA Eligibility
Employers must have fewer than 100 employees and cannot offer another retirement plan.
Contribution Limits for Simple IRAs (2025)
- Employee: Up to $16,500 per year for individuals under 50.
- Employees aged 50 and above can contribute an additional $3,500 as a catch-up contribution.
- Employees aged 60 to 63 can take advantage of a new “super” catch-up contribution of $5,250.
- Employer: Must choose between:
- Matching up to 3% of the employee’s compensation.
- A 2% non-elective contribution for all eligible employees.
Simple IRA Vesting
Contributions are 100% immediately vested.
Administrative Requirements for a Simple IRA
- No annual Form 5500 filing required.
- Fewer compliance requirements compared to a 401(k).
Withdrawals from Simple IRAs
Penalty-free at 59½, but withdrawals within the first two years of participation are subject to a 25% penalty.
SEP IRA
A Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA is designed for self-employed individuals and small businesses.
SEP IRA Eligibility
Any business owner with one or more employees or self-employed individuals.
SEP IRA Contribution Limits (2025)
- Employees: Employees cannot contribute to a SEP IRA; only employers make contributions.
- Employer: Contributions are limited to 25% of the employee’s compensation, up to $70,000.
SEP IRA Vesting
Contributions are 100% immediately vested.
Administrative Requirements for SEP IRAs
- No annual Form 5500 filing.
- Minimal compliance or reporting requirements.
Withdrawals from SEP IRAs:
Penalty-free at 59½. Early withdrawals are subject to a 10% penalty plus income tax.
The Tax Implications for Each Retirement Plan
Each plan offers tax advantages for both employers and employees:
401(k):
- Employee contributions are tax-deferred, reducing taxable income in the year contributed.
- Employer contributions are tax-deductible.
- Withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income in retirement.
SIMPLE IRA:
- Contributions (both employee and employer) are pre-tax, reducing taxable income.
- Withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income.
SEP IRA:
- Employer contributions are tax-deductible for the business and excluded from employee income until withdrawal.
- Withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income in retirement.
Retirement Plan Benefits for Business Owners
For employers, contributing to a retirement plan can be more cost-effective than offering salary raises. For example, increasing employer matching contributions instead of wages reduces payroll tax obligations and provides employees with long-term financial benefits.
As a business owner, offering a retirement plan can benefit you and your employees significantly. For you, a retirement plan can serve as a valuable tool for saving for your own future, while also offering tax advantages that can help reduce your business’s taxable income. By providing a retirement plan, you can attract and retain high-quality employees, as well as increase employee satisfaction and loyalty.
For your employees, a retirement plan can provide a way to save for their future and build financial security, while also offering the potential for employer matches or contributions. Overall, offering a retirement plan can be a win-win for both business owners and employees, providing valuable benefits and helping to build a strong financial foundation for the future.
Additional Resources for Individual Retirement Savings
If your workplace doesn’t offer a retirement plan, or if you want to save more for retirement, you can open a Traditional or Roth IRA independently. For 2025, the contribution limit for IRAs remains at $7,000, with an additional $1,000 catch-up contribution allowed for individuals aged 50 and over.
New Developments in Retirement Planning
The SECURE Act 2.0 introduced several new features, including the option for employees to request that employer matching contributions go toward student loans instead of retirement savings. This provision, effective in 2024, addresses the challenge of balancing student debt repayment with retirement planning.
Tools and Services for Implementation
Setting up and managing a retirement plan can be simplified with the right tools and services:
- Financial Institutions: Banks, brokerage firms, and online platforms offer turnkey solutions for small businesses to establish and manage retirement plans efficiently.
- Payroll Providers: Some payroll service providers integrate payroll with retirement plan contributions, automating compliance and simplifying contributions.
- Retirement Plans Startup Costs Tax Credit: Businesses starting a new retirement plan may qualify for a tax credit covering up to $5,000 annually for three years, plus an additional $500 annually for auto-enrollment plans.
- Consulting Services: Financial advisors and CPAs can guide businesses in choosing and implementing the best retirement plan for their specific needs and circumstances.
Choosing the Right Plan for Your Business
The best plan for your business depends on its size, resources, and workforce needs:
- 401(k): Ideal for larger businesses looking to attract and retain top talent with higher contribution limits and flexible plan options.
- SIMPLE IRA: Suited for small businesses prioritizing simplicity and cost-effectiveness over higher contribution limits.
- SEP IRA: A strong choice for self-employed individuals or small businesses with fluctuating income, as contributions are discretionary.
For individual savers, combining workplace plans with independent IRAs can help maximize savings and tax advantages, ensuring a diversified and robust retirement strategy.
Choosing between a 401(k), SIMPLE IRA, and SEP IRA requires a thorough understanding of each plan’s unique features and limitations. With updated 2025 contribution limits, the flexibility of Roth options, and tax credits for startups, there are more opportunities than ever to build a retirement plan tailored to your needs.
By considering your business size, employee preferences, and long-term financial goals, you can make an informed decision that secures a better future for both you and your team. Consulting financial professionals and leveraging available tools will ensure your retirement strategy is efficient and effective. Start planning today to take full advantage of the benefits these plans have to offer.
Volpe Consulting and Accounting provides tax planning services for all those wondering which plan to choose and how it affects your personal situation.